ZOOM ON THE EFG METHOD
The EFG method, also known as melt pulling, growth pot or simply CZ, is a single crystal growing technology with which pure single crystal materials can be synthesised.
The process was developed in 1918 by the Pole Jan Czochrolski.
A purified melt of a certain material (sapphire crystals, for example) is placed in a crucible. From the top, a seed (inoculation) oriented and attached to a slowly rotating metal rod is plunged into the melt, which is then slowly withdrawn upwards again, while the melt solidifies at the forming interface following overcooling. By varying and decreasing the speed and temperature, the crystal grows.
The column of crystal is called an “ingot”.
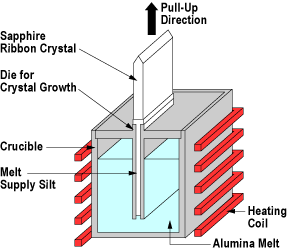
The Stepanov process is a modified CZ process, known in the USA as EFG (edge-defined film-fed growth). In this technique, a mask is applied to the surface, or a matrix is placed in the melt. Special shapes include sapphire strips (substrates for integrated circuits), sapphire single crystals with a predetermined cross-section and sapphire tubes (lasers, high-pressure lamps, etc.).